Saturday, March 3, 2012
Thursday, March 1, 2012
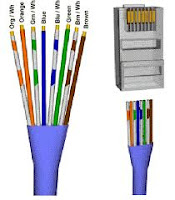
CAT5 CABLE AND RJ45 CONNECTOR
The CAT-5 is a standard cable which has four twisted pairs of colours. It is easy to crimp a RJ45 connector to CAT-5 cable and make it into a straight cable or cross the cable as required. To make a straight cable, the ends must be crimped in the same way at each end. When making a crossover cable, some wires of certain colours have to be reversed.
CAT-5 cable is usually divided into 4 twisted pairs of colours:
Orange
Green / green-white
Blue / white and blue
Brown / brown-white
Green / green-white
Blue / white and blue
Brown / brown-white
Straight Cable Colour Code
To make a straight cable, the tips must be crimped typically the same way ateach end by respecting the twisted pair size.
In general, the colour code used is:
1) orange-white
2) orange
3) green-white
4) Blue
5) blue-white
6) Green
7) brown-white
8) brown
Crossover Cable Colour Code
For a crossover cable, swap 1 with 3, and 2 with 6, in the list above. This gives:
1) green-white
2) green
3) orange and white
4) Blue
5) blue-white
6) orange
7) brown-white
8) brown
Standard EIA / TIA 568 (A &B) Colour Code
Straight cable
1) white-green / white-green
2) green / green
3) white-orange / white-orange
4) Blue / blue
5) white-blue / white-blue
6)Orange
7) white-brown / white-brown
8) brown / brown
1) white-green / white-green
2) green / green
3) white-orange / white-orange
4) Blue / blue
5) white-blue / white-blue
6)
7) white-brown / white-brown
8) brown / brown
Crossover cable 10/100baseT Colour Code
1) white-green / white-orange
2) Green / orange
3) white-orange / white-green
4) Blue / blue
5) white-blue / white-blue
6) Orange / green
7) white-brown / white-brown
8) brown / brown
Complete crossover cable or crossgigabit Colour Code
On Gbic 1000BaseT eg
1) white-green / white-orange
2) Green / orange
3) white-orange / white-green
4) Blue / white-brown
5) white-blue / brown
6) Orange / green
7) white-brown / blue
8) Brown / white-blue
Note:
Many Gigabits (10/100/1000 multi speed) are auto MDI / MDIX and automatically adapt to the type of cable connected.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Labels
- 2
- accounts package
- Active X Problem
- BATCH FILE
- CAT5 and RJ45 CONNECTOR
- COMMAND PROMPT TRICKS
- Computer Tips
- downloads
- Duplicate Signature
- eMo error
- Fast installation of XP
- Increase Browsing speed
- Meghdoot
- Meghdoot7.0
- MSDTC ERROR
- NL upgradation error
- nregamo db cration
- plierror patch
- POSTMAN NAME CHANGE ERROR
- Printing through USB printer
- Recovery db tools
- RNet Comm Error Solution
- RPC ERROR SOLUTION
- Sanchaypost
- Save time with computer shortcuts
- source microsoft.com
- speednet solution1
- SQL
- SQL 2008 Problem Solution
- sql 2008 r2 point of sale
- sql uninstallation
- SQLexpress
- supervisor
- Suspected database repair
- Sys Restore Process in windows 7
- System Corrupt
- System32 config system error
- Task Manager Disabled
- Update 5 eMO upgradation error
- Update-3 error
- Update3 error